[HL-12] Review of (max) heap
- What is a heap?
- Structure of a heap
- Push a new element
- Pop the (max) element
- Two ways to build a heap
What is a heap?
Heap is a very useful data structure for priority queues.
- quickly find minimum or maximum element, even after we add or remove an element from it.
- a very dynamic data structure similar to a Queue but not in FIFO order.
- The order is based on the priority property.
Structure of a heap
- A complete binary tree
- Meet heap condition: values of children nodes are not greater than that of their parent node.
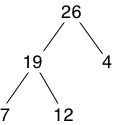
- Such as,
- Standard implementation by using an array:

- A[i] is the parent node of A[2*i] (left child) and A[2*i+1] (right child), assume that we leave the first element A[0] empty.
- Then, the heap condition becomes: A[i] <= A[i/2] for all i in [1,…,n-1].
Push a new element
- Insert a new element 30,

- First, add it into the first empty position at the end;
- Then, do "climb up" for the new element, until it becomes the root or its value is less than or equal to the value of its parent node.
Pop the (max) element
- Delete the root (max element),
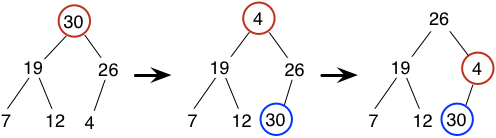
- First, swap the root with the last element;
- Then, do "sift down" for the root, until it becomes a leave or its value is greater than or equal to that of its children nodes.
Two ways to build a heap
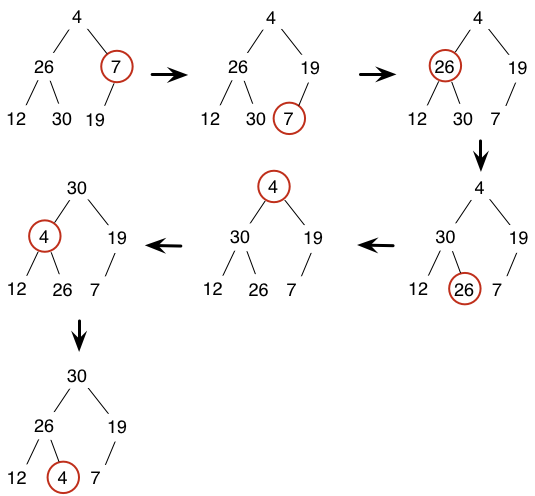
Let’s assume that the sequence is 4, 26, 7, 12, 30, 19.
- Repeatedly insert new element (O(nlogn)):
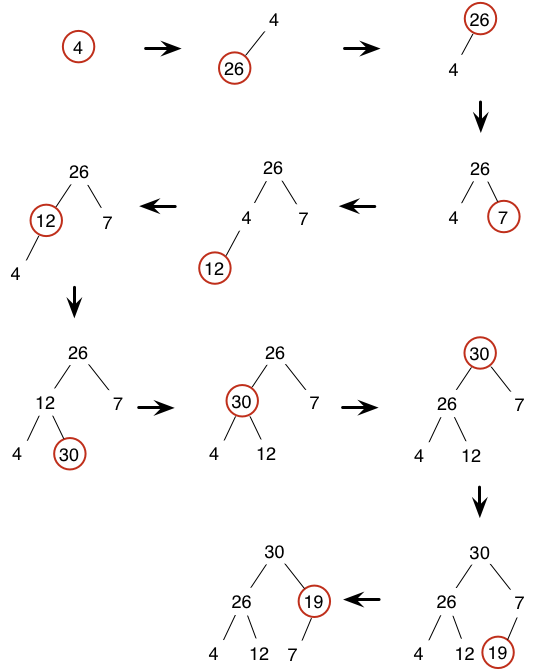
- A bottom-up approach (O(n)): first, put all elements into the complete tree at first;
- Then, “sift down” every parent node from the last one to the root (note: it is incorrect to start from the root, why?).